
Ways to Invest Money: Real Estate, Gold, or Dividend Stocks?
Investing is a crucial component of financial planning and wealth building. It allows individuals to grow their wealth over time, protect against inflation, and achieve financial goals such as retirement, purchasing a home, or funding education.
Diversification, the practice of spreading investments across various asset classes, is vital to managing risk and optimizing returns. By diversifying, investors can mitigate the impact of poor performance in any single investment, thus stabilizing their portfolio.
Investing in Real Estate
Real estate investment involves purchasing properties to generate rental income or capital gains.
This tangible asset class includes residential properties (such as single-family homes and apartments), commercial properties (like office spaces and shopping centers), and industrial properties (such as warehouses and factories).
Benefits of Investing in Real Estate
- Passive Income: Real estate can provide a steady stream of rental income, contributing to a stable cash flow.
- Appreciation: Property values can increase over time, offering the potential for significant capital gains upon sale.
- Tax Advantages: Investors can benefit from various tax deductions, including mortgage interest, property depreciation, and maintenance expenses.
- Diversification: Real estate adds a tangible asset to an investment portfolio, helping to diversify and reduce overall risk.
Potential Risks and Considerations
- High Initial Capital: Purchasing property requires substantial upfront capital, including down payments, closing costs, and renovations.
- Liquidity: Real estate is not as liquid as stocks or bonds, meaning it can take time to sell a property and access funds.
- Market Fluctuations: Property values can be affected by economic conditions, interest rates, and local market trends.
- Management Responsibilities: Owning real estate involves ongoing maintenance, dealing with tenants, and potential legal issues.
Investing in Gold
Gold has been valued as a form of currency and a store of wealth for centuries. It is often viewed as a "safe haven" asset during times of economic uncertainty and market volatility.
Historically, gold has maintained its value over long periods, making it a reliable hedge against inflation and currency devaluation.
Advantages of Including Gold in an Investment Portfolio
- Stability: Gold is known for its ability to retain value, especially during economic downturns.
- Inflation Hedge: As a tangible asset, gold tends to increase in value as inflation rises, protecting purchasing power.
- Diversification: Adding gold to a portfolio can help reduce overall risk, as its price movements often have a low correlation with other asset classes like stocks and bonds.
Potential Downsides to Investing in Gold
- No Income Generation: Unlike stocks or real estate, gold does not produce dividends or rental income.
- Storage and Security: Physical gold requires secure storage, which can involve additional costs.
- Volatility: Gold prices can be volatile in the short term, influenced by geopolitical events, currency fluctuations, and changes in investor sentiment.
Investing in Dividend Stocks
Dividend stocks are shares of companies that regularly return a portion of their earnings to shareholders in the form of dividends.
These payments can be made monthly, quarterly, or annually and are typically issued by well-established companies with a stable financial performance.
Dividend stocks are an attractive option for investors seeking regular income in addition to potential capital appreciation.
Benefits of Choosing Dividend Stocks for Investment
- Regular Income: Dividend stocks provide a steady stream of income, which can be particularly useful for retirees or those looking to supplement their income.
- Potential for Capital Appreciation: Besides receiving regular dividend payments, investors can also benefit from the appreciation of the stock's value over time.
- Lower Volatility: Dividend-paying stocks tend to be less volatile than non-dividend-paying stocks, as they are often associated with more established, financially stable companies.
- Tax Advantages: In many jurisdictions, qualified dividends are taxed at a lower rate compared to ordinary income, providing a tax-efficient way to earn incomeâ.
Monthly Dividend Stocks
Monthly dividend stocks distribute dividends every month, offering a more frequent income stream compared to the typical quarterly or annual payouts. This can be particularly advantageous for investors who rely on dividend income for their living expenses, as it aligns better with monthly financial needs.
Highlight on High-Yielding Monthly Dividend Stocks
A high-yielding dividend stock is one that offers a higher-than-average dividend yield, which is calculated by dividing the annual dividend payment by the stock's current price. High yields can be attractive, but they also come with higher risks, as they may indicate underlying issues within the companyâ.
Examples of Highest Yielding Monthly Dividend Stocks
- Realty Income Corporation (O): Known as "The Monthly Dividend Company," Realty Income has a long history of paying reliable monthly dividends.
- STAG Industrial (STAG): This company focuses on single-tenant industrial properties and consistently pays monthly dividends.
- Pembina Pipeline Corporation (PBA): A Canadian pipeline company offering robust monthly payoutsâ.
The performance of high-yielding monthly dividend stocks depends on several factors:
- Earnings Stability: Companies with consistent and predictable earnings are more likely to maintain their dividend payouts.
- Payout Ratio: A moderate payout ratio indicates that a company is not overextending itself and can sustain its dividends even during economic downturns.
- Industry Conditions: The overall health of the industry in which the company operates can affect its ability to generate profits and pay dividends.
- Economic Environment: Broader economic conditions, including interest rates and inflation, can impact the performance and attractiveness of dividend stocksâ.
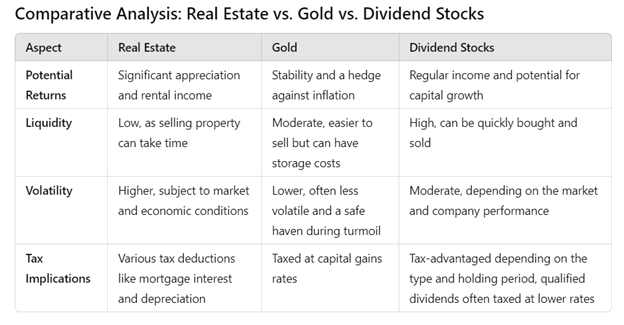
Endnote: How to Choose the Right Investment
Choosing the right investment depends on individual financial goals, risk tolerance, and market conditions:
- Financial Goals: Determine whether you need regular income, long-term growth, or a hedge against inflation.
- Risk Tolerance: Assess your comfort with potential losses and market volatility.
- Market Conditions: Consider the current economic environment and how different asset classes are performingââ.
By evaluating these factors and understanding the unique characteristics of real estate, gold, and dividend stocks, investors can make informed decisions to build a diversified portfolio that aligns with their financial objectives.





