There are no statistics on how widespread prostate cancer is in Nepal, but the number of patients with this disease is increasing day by day. This shows the longevity of men, the widespread use of PSA blood tests, the significant increase in the number of specialist medical urologists, the increased awareness of health and modern equipment (CT scans, MRIs and prostate fibrosis testing) available within the country. At present, no need to go abroad for the identification and treatment of this disease.
Causes of prostate cancer:
According to world statistics, men have prostate cancer after lung cancer. It is most commonly identified in men over the age of 50. The autopsy of men who have died before the age of 80 shows that 50% of the disease is in an unsuitable condition. The widespread disease caused by prostate cancer is still unclear to scientists. The male hormone somehow plays an important role in the origin of the disease. Apart from this, humans also have some role to play in ethnic, geographical, environmental and genetic diversity.
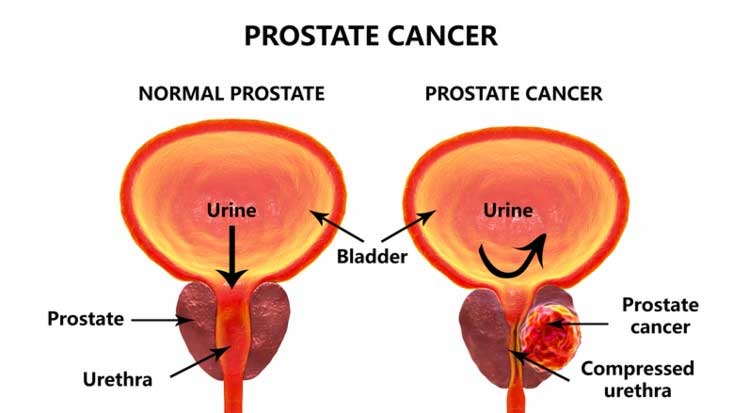
The prostate is made up of muscles, fibrous and glandular fibers. Prostate cancer is a disease of the glandular tissue. In the initial stage, the pain is spread to the prostate gland. But while sitting, this gland can spread out to the lymphatic gland, bone, lungs, brain, liver. The answer to the question of how quickly prostate cancer can spread to the body depends on the results of the test. Prostate cancer is not a rapidly spreading disease. Its natural development takes about 10-15 years. In the age at which most prostate cancer occurs, many men suffer from heart, liver, kidney, lung, diabetes, high blood pressure, etc. Therefore, more than 80 percent of men who suffer from prostate cancer can die from other diseases before they spread to different parts of the body.
PSA and Prostate Cancer:
The prostate gland is a protein made by cells - PSA. This is an essential element of ejaculation, not ejaculation. In the absence of PSA, Venus cannot swim in semen and is unable to fertilize the ovaries. Prostate cancer cells can also produce PSA, just like normal cells in the prostate gland but to a lesser extent. Although PSA production is not high in patients with prostate cancer, this factor increases the blood sugar level and increases blood volume.
PSA is not a special ingredient in prostate cancer, but if the blood levels of this element are high, the development of cancer in the prostate gland can help to determine whether the disease has started. In some types of prostate cancer, PSA blood levels may not increase, such as neuroendocrine tumors - this is very severe prostate cancer, but PSA tests are not detected. PSA blood levels do not increase in prostate cancer in the early part of the urethra. Prostate Cancer One month after the main surgery, it should be considered that prostate cancer surgery is not complete, not far below the PSA's blood levels. Since the PSA's blood tests began in the medical field in 1986, millions of prostate cancer patients have been identified and have a key role in the treatment and monitoring.
PSA is not an indicator of prostate cancer, but in cases of cancer, PSA is elevated in the bloodstream. Do not take the PSA test as a definitive test to determine whether there is prostate cancer such as a fibroid test. The final decision whether or not to have prostate cancer and to find out how dangerous and severe that cancer is should be considered the definitive prostate tissue test.
Four pillars of prostate cancer diagnosis:
- The age of the patient
- Finger check from the rectum of the prostate gland
- PSA blood level test
- Tubular examination of the prostate gland.
After diagnosing cancer with the above mentioned four intensive tests, various other tests must be performed to ascertain whether the tumor is confined to the prostate gland or is spread out. Blood and urine tests, X-rays, ultrasonography, city scans, MRIs, radiation tests of entire bone markers, etc. have their own important place in the diagnosis, treatment, monitoring and complete management of common to most complex tests.
Role of Consulting:
Counseling has a profound role in the treatment and management of prostate cancer. Patients should be consulted about the risk of prostate cancer in words they understand. In more than 80 percent of the patients, the prostate tumor does not become malignant and the disease progresses over a long period of time. Such illnesses will result in other complex diseases. Less than 20 percent of prostate tumors are fatal and the patient dies from the disease. How the tumor develops in the patient and which the patient is eligible for radical surgery or radiation therapy that can eradicate cancer should be selected in a mature way.
Prostate Cancer Symptoms:
In the beginning, the disease is completely symptomless. The symptoms that develop after the disease develops are not so specific. The effects of urine velocity may also be associated with conditions such as general prostate hyperplasia, urinary tract infection, urethral contraction. But when urination is difficult to prevent, blood in urine and semen, painful ejaculation, decreased sexual desire, prostate cancer needs to be tested to make sure it is not the cause. If the prostate cancer spreads beyond the gland, then there may be vague and uncertain symptoms such as lumbar and bone soreness, bone breakdown with slight injuries, loss of body weight, swelling of the kidneys, loss of muscle-kidney function. In short, there is no specific symptom of prostate cancer. To prove that there is prostate cancer, the cancer cells must be identified in the tissue from the prostate gland. The purpose of modern health testing is to identify the disease as early as possible and manage it according to the latest scientific achievement.
Main treatment methods:
Disease elimination treatment:
Tumor elimination treatment involves the operation of a qualified candidate for complete prostate and some organs. For this purpose, irradiated prostate cells are rendered ineffective by radiation to a patient unfit or unwilling to accept surgery.
Palliative treatment of the disease:
The treatment of patients who have been excluded from the tumor is only short-lived. Such treatment methods include surgery, hormones, radiation, and chemicals. These methods are used alone, in combination with two or more methods. Despite these modern and valuable treatments, cancer soon afterward faces severe adverse conditions and spreads aggressively. The expected life expectancy of a patient should be at least 10 years after cancer eradication treatment. Active surveillance during and after the treatment of prostate cancer is extremely important.
-Prof. Dr. Arjundev Bhatt
(The author is a Senior Consultant Urologist.)





