
Project Planning 101: Things to Know
Project planning is the process of defining the scope, objectives, and steps necessary to complete a project.
It involves outlining tasks, timelines, resources, and responsibilities to ensure that a project is completed on time, within budget, and to the desired quality standards.
Effective project planning provides a roadmap for project execution and serves as a reference point throughout the project lifecycle.
Benefits of Effective Project Planning
Effective project planning offers several benefits:
- Clear Direction: It provides a clear roadmap for project execution, helping team members understand the project goals and the steps required to achieve them.
- Resource Management: It ensures optimal allocation and utilization of resources, reducing waste and avoiding resource shortages.
- Risk Mitigation: By identifying potential risks early, it allows for the development of strategies to mitigate or avoid these risks.
- Improved Communication: It facilitates better communication among team members and stakeholders, ensuring that everyone is on the same page.
- Enhanced Efficiency: It helps in organizing tasks and setting priorities, leading to more efficient project execution and time management.
- Accountability: It assigns specific roles and responsibilities, making it easier to track progress and hold team members accountable for their tasks.
Key Elements of Project Planning
The first step in project planning is to define the project goals and objectives. Goals are broad primary outcomes, while objectives are specific, measurable steps that need to be accomplished to achieve these goals.
Clear and well-defined objectives help in maintaining focus and direction throughout the project. Using the S.M.A.R.T. criteria (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) can help in setting effective objectives.
Identifying Stakeholders and Their Requirements
Stakeholders are individuals or groups who have an interest in the project’s outcome. Identifying stakeholders and understanding their needs and expectations is crucial for the project's success.
Engaging with stakeholders through meetings, interviews, and workshops can help gather their requirements and ensure that the project aligns with their interests. This engagement also helps in securing their support and managing their expectations.
Establishing the Project Scope and Deliverables
The project scope defines the boundaries of the project, including what will and will not be included. Establishing a clear scope helps prevent scope creep and ensures that the project team understands what is expected.
Deliverables are tangible or intangible outputs produced as a result of the project. Defining deliverables clearly ensures that all stakeholders have a mutual understanding of what the project will achieve.
Creating a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
A Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) is a hierarchical decomposition of the project into smaller, more manageable components. It breaks down the project into work packages, tasks, and subtasks.
The WBS helps in organizing and defining the total scope of the project, making it easier to assign tasks, estimate costs, and schedule activities. It serves as the foundation for project planning, budgeting, scheduling, and resource allocation.
Steps to Create an Effective Project Plan
- Define the Project Scope and Objectives: Clearly outline the project’s purpose, goals, and deliverables. Ensure that objectives are specific and measurable.
- Identify Stakeholders and Requirements: Engage with stakeholders to understand their needs and expectations. Document these requirements to ensure alignment.
- Develop a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS): Break down the project into smaller components, tasks, and subtasks. Assign responsibilities and estimate the resources needed for each task.
- Create a Project Schedule: Develop a timeline for the project using tools like Gantt charts. Identify task dependencies and set milestones to track progress.
- Allocate Resources: Identify the necessary resources, including personnel, equipment, and materials. Ensure that resources are allocated efficiently and consider any constraints.
- Establish a Budget: Estimate the costs associated with each task and develop a project budget. Monitor expenses to ensure that the project remains within budget.
- Develop a Risk Management Plan: Identify potential risks and develop strategies to mitigate them. Include contingency plans to address unexpected issues.
- Create a Communication Plan: Define how information will be communicated among team members and stakeholders. Establish regular check-ins and reporting mechanisms.
- Document the Project Plan: Compile all the elements into a comprehensive project plan document. Ensure that it is easily accessible and shared with all relevant parties.
- Monitor and Adjust: Continuously monitor the project’s progress and make adjustments as necessary. Use the project plan as a reference to keep the project on track.
Tools and Techniques for Project Planning
Several tools and techniques can facilitate effective project planning, including:
- Gantt Charts: Visualize the project timeline and track progress.
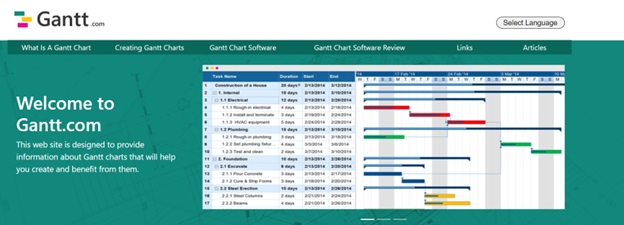
- Project Management Software: Tools like Microsoft Project, Trello, Asana, and Wrike help manage tasks, resources, and schedules.
- Risk Assessment Tools: Techniques like SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) and risk matrices help identify and evaluate potential risks.
- Communication Tools: Platforms like Slack, Microsoft Teams, and Zoom facilitate communication and collaboration among team members and stakeholders.
Managing Resources and Budget
Proper resource identification and allocation are critical components of effective project planning. Resources can include personnel, equipment, materials, and technology. Begin by listing all resources required for each task in the project.
Assign resources based on availability, skills, and project needs. Resource allocation ensures that each team member knows their responsibilities and has the tools needed to complete their tasks.
Budgeting for Project Activities
Creating a detailed budget involves estimating the costs associated with each project activity. This includes direct costs such as labor, materials, and equipment, as well as indirect costs like administrative expenses.
A well-defined budget helps in monitoring expenditures and ensuring that the project stays within financial constraints. Regularly compare actual expenses against the budget to identify and address any variances promptly.
Techniques for Managing Resource Constraints
Resource constraints can pose significant challenges during project execution. Techniques to manage these constraints include:
- Resource leveling: Adjusting the project schedule to address resource limitations, ensuring that no resources are over-allocated.
- Resource smoothing: Adjusting activities to maintain resource usage within predefined limits while keeping the project on track.
- Prioritizing tasks: Focus on critical tasks and allocate resources accordingly, delaying less critical tasks if necessary.Scheduling and Timeline Management
A project schedule outlines the timeline for completing tasks and achieving milestones. Start by defining all tasks and estimating their duration.
Sequence the tasks based on dependencies, identifying which tasks must be completed before others can begin. This helps in creating a logical flow for the project activities.
Gantt charts are valuable tools for visualizing the project schedule. They display tasks along a timeline, showing start and end dates, task durations, and dependencies. Other scheduling tools include:
Critical Path Method (CPM): Identifies the sequence of critical tasks that determine the project duration.
PERT (Program Evaluation and Review Technique): Uses statistical methods to estimate task durations and project timelines, accounting for uncertainties.
Regularly monitor the project’s progress against the schedule. Use project management software to track task completion, identify delays, and adjust timelines as needed. Implementing a robust monitoring system allows for early detection of schedule deviations, enabling corrective actions to keep the project on track.
Risk Management in Project Planning
Risk management starts with identifying potential risks that could impact the project. This involves brainstorming sessions, reviewing historical data, and consulting with experts. Common risks include budget overruns, resource shortages, technical challenges, and external factors like regulatory changes.
Developing Risk Mitigation Strategies
Once risks are identified, develop strategies to mitigate them. This can include:
- Risk avoidance: Altering the project plan to eliminate the risk.
- Risk reduction: Taking steps to reduce the likelihood or impact of the risk.
- Risk transfer: Shifting the risk to a third party, such as through insurance or outsourcing.
- Risk acceptance: Acknowledging the risk and preparing contingency plans.
Importance of Contingency Planning
Contingency planning involves preparing for potential risks by developing backup plans. Allocate a contingency budget and time buffers to address unexpected issues.
Contingency plans ensure that the project can continue smoothly despite unforeseen challenges, minimizing disruptions and maintaining project momentum.
Communication and Collaboration
A communication plan is essential for ensuring that all project stakeholders are informed and engaged throughout the project lifecycle.
This plan should outline how information will be disseminated, who will be responsible for communication, and the frequency of updates. Key components of a communication plan include:
- Stakeholder Analysis: Identifying all stakeholders and their information needs.
- Communication Methods: Choosing appropriate communication channels (e.g., emails, meetings, reports).
- Frequency: Establishing how often updates will be provided (e.g., weekly status reports, monthly progress meetings).
- Responsibility: Assigning team members to handle specific communication tasks.
Tools for Effective Team Collaboration
Effective collaboration is crucial for project success. Utilizing the right tools can enhance team coordination and productivity. Some popular collaboration tools include:
Slack
Slack facilitates real-time communication through channels, direct messages, and group chats. It integrates seamlessly with various project management tools, allowing team members to share files, links, and updates instantly. Slack's notification system ensures that team members stay informed about important project developments.
Microsoft Teams
Microsoft Teams offers a comprehensive suite of collaboration features, including chat, video conferencing, and file-sharing capabilities.
Teams can create dedicated channels for different projects or departments, enabling organized and focused discussions. Integration with Microsoft Office apps allows for easy document editing and sharing within the platform.
Trello
Trello provides a visual approach to project management with boards, lists, and cards. Each board represents a project, lists represent stages of the project, and cards represent tasks.
This intuitive system helps teams track progress, assign tasks, and set deadlines. Trello's flexibility and ease of use make it ideal for managing both simple and complex projects.
Asana
Asana helps teams organize tasks, track progress, and manage workloads efficiently. It allows for the creation of tasks and subtasks, assignment of responsibilities, and setting of due dates.
Asana's timeline view provides a clear overview of project schedules, making it easier to manage deadlines and dependencies. Asana's reporting features enable teams to monitor performance and productivity.
Ensuring Stakeholder Engagement
Engaging stakeholders is vital to ensure their support and to meet their expectations. Techniques for stakeholder engagement include:
- Regular Updates: Keep stakeholders informed through consistent communication.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Provide channels for stakeholders to give input and feedback.
- Involvement in Decision-Making: Involve key stakeholders in important project decisions to foster a sense of ownership and commitment.
How to Optimize Your Project Planning
To optimize project planning, consider implementing the following best practices:
- Set Clear Objectives: Ensure that project goals and objectives are well-defined and communicated to all team members.
- Use a Structured Approach: Follow a structured project management methodology, such as Agile, Waterfall, or Hybrid, to guide your planning process.
- Leverage Technology: Utilize project management software to streamline planning, scheduling, and resource allocation.
- Maintain Flexibility: Be prepared to adapt your plan as project requirements and circumstances change.
Tips for Continuous Improvement in Project Management
Continuous improvement is key to long-term project success. Here are some tips to foster continuous improvement:
- Conduct Post-Project Reviews: Analyze what went well and what could be improved after project completion.
- Solicit Feedback: Regularly seek feedback from team members and stakeholders to identify areas for enhancement.
- Invest in Training: Provide ongoing training and development opportunities for your project team.
- Implement Lessons Learned: Apply lessons learned from past projects to improve future planning and execution.

Recommended Resources and Tools
Several resources and tools can aid in optimizing project planning:
- Project Management Institute (PMI): Offers resources, certifications, and standards for project management.
- PMBOK Guide: A comprehensive guide to project management best practices.
- Online Courses: Platforms like Coursera, Udemy, and LinkedIn Learning provide courses on project management.
- Project Management Software: Tools like Wrike, Monday.com, and Smartsheet can enhance project planning and execution.
Key Takeaways
Project planning is the foundation of successful project execution. It provides a clear roadmap, ensures efficient resource utilization, mitigates risks, and facilitates effective communication and collaboration.
Investing time and effort in thorough project planning, sets the stage for achieving project goals and delivering high-quality results.
Applying best practices in project planning, staying flexible, and continuously seeking improvement can lead to more successful project outcomes.





