
The brain is one of the most complex and fascinating organs in the human body. It is the control center that coordinates all the functions of the body and is responsible for thought, emotion, sensation, movement, and behavior. The brain is made up of billions of neurons and synapses, which work together to form intricate neural circuits. Understanding the anatomy and structure of the brain, as well as the role of neurons and synapses in brain function, is critical for unlocking the mysteries of this amazing organ.
Anatomy and Structure of the Brain
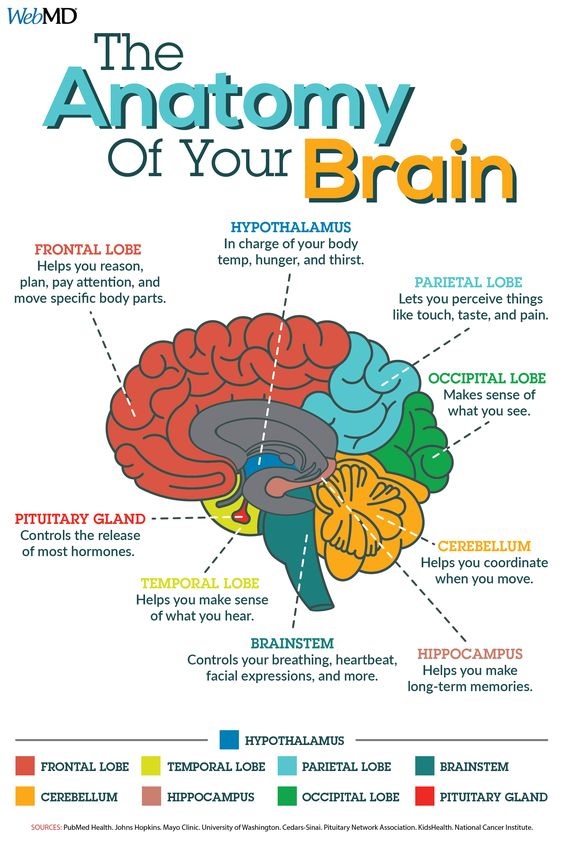
The human brain is divided into three main parts: the cerebrum, the brainstem, and the cerebellum. The cerebrum is the largest and most complex part of the brain, and it is responsible for consciousness, thought, emotion, sensation, and voluntary movement. The brainstem connects the cerebrum to the spinal cord and is responsible for controlling many unconscious functions, such as breathing and heartbeat. The cerebellum is located at the base of the brain and is responsible for coordination and balance.
Role of Neurons and Synapses in Brain Function
The brain is made up of billions of neurons, which are specialized cells that transmit information throughout the brain and the rest of the body. Neurons communicate with each other through synapses, which are specialized structures that allow neurons to transmit information to each other. When a neuron receives a signal from another neuron, it generates an electrical signal that travels along its axon, eventually reaching the synapse. At the synapse, the electrical signal triggers the release of chemicals called neurotransmitters, which cross the synapse and bind to receptors on the next neuron, transmitting the signal to the next neuron. This process of transmitting signals from one neuron to another is called synaptic transmission, and it is the basic mechanism by which neurons communicate with each other.
Latest Advancements and Research in the Field of Brain Science
Over the past few decades, there have been many advancements and breakthroughs in the field of brain science. One of the most exciting areas of research is the study of neuroplasticity, or the ability of the brain to rewire its neural circuits in response to new experiences. This has led to new insights into the way the brain learns and adapts to new experiences, and has important implications for understanding and treating brain-related disorders.
Another exciting area of research is the study of brain-computer interfaces, which use technology to connect the brain directly to computers or other devices. This technology has the potential to revolutionize the way we interact with computers and has important implications for the fields of medicine, education, and gaming.
Functions of Different Regions of the Brain
Each region of the brain is responsible for specific functions, and the functions of different regions of the brain are highly interconnected. Some of the most important regions of the brain include the frontal lobe, which is responsible for decision-making, problem-solving, and planning; the parietal lobe, which is responsible for sensation, perception, and movement; the temporal lobe, which is responsible for hearing, language, and memory; and the occipital lobe, which is responsible for vision.
Impact of Environmental and Lifestyle Factors on Brain Function
The brain is highly sensitive to environmental and lifestyle factors, and these factors can have a profound impact on brain function. For example, stress and anxiety can have a negative impact on brain function, while exercise and a healthy diet can improve brain function and reduce the risk of brain-related disorders. Environmental factors such as exposure to toxins, such as lead or mercury, can also have a negative impact on brain function, and it is important to be aware of these factors in order to maintain optimal brain function and prevent brain-related disorders. Here are some examples of environmental and lifestyle factors that can impact the brain:
- Lack of Sleep: Sleep is essential for the brain to repair and consolidate memories. Chronic sleep deprivation can lead to cognitive decline, memory loss, and an increased risk of dementia.
- Poor Diet: A diet that is high in unhealthy fats, sugar, and processed foods can lead to inflammation in the brain, which can damage the delicate neural connections that are crucial for proper brain function. On the other hand, a diet that is rich in fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats has been shown to support brain health and reduce the risk of cognitive decline.
- Chronic Stress: Chronic stress has been linked to an increased risk of depression, anxiety, and cognitive decline. This is because stress can alter the brain's neurochemical balance, leading to an increase in the release of stress hormones that can damage the brain's delicate neural circuits.
- Alcohol and Substance Abuse: Excessive alcohol consumption and substance abuse can lead to brain damage and cognitive decline. Alcohol, for example, is toxic to brain cells and can disrupt the brain's normal functioning, leading to memory loss, confusion, and impaired judgment.
- Lack of Physical Activity: Physical activity has been shown to have a positive impact on brain function. Regular exercise increases blood flow to the brain, which supplies it with the necessary nutrients and oxygen to support its functioning. Exercise has also been shown to increase the production of new neurons and promote neuroplasticity, the brain's ability to rewire its neural circuits in response to new experiences.
It is clear that environmental and lifestyle factors can have a significant impact on brain function, and it is important to be aware of these factors in order to maintain optimal brain health. By making healthy lifestyle choices, such as eating a balanced diet, getting enough sleep, and engaging in regular physical activity, you can help to support your brain's functioning and reduce the risk of cognitive decline and brain-related disorders.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the brain is a complex and fascinating organ that is responsible for coordinating all the functions of the body. Understanding the inner workings of the brain can provide valuable insight into its functions and the various factors that can impact its performance. From its intricate neural circuits and synaptic transmission to its ability to rewire its neural connections in response to new experiences, the brain is truly a marvel of nature. By continuing to research and understand the intricacies of the brain, we can gain a better understanding of its functions and find ways to support its health and wellbeing.
Health Mental Health




