How to Apply Social Learning Theory in Education: Learn Actionable Strategies
Have you ever found yourself learning better by watching someone else do something? Whether it's a child observing their parents or students collaborating in a group, learning through observation is one of the most natural and effective ways to absorb new information. This concept lies at the heart of Social Learning Theory, introduced by psychologist Albert Bandura.
Social Learning Theory highlights how we learn by observing, imitating, and modeling others' behaviors. It bridges the gap between behavioral and cognitive theories, showing how people acquire new skills and attitudes through social interactions. This approach offers educators a powerful toolkit to engage students, encourage collaboration, and create dynamic learning experiences.
This article will explore how Social Learning Theory works, why it matters in education, and practical strategies to apply it in the classroom. You'll also find real-life examples, solutions to everyday challenges, and actionable advice to help you get started.
What is Social Learning Theory?

Albert Bandura developed Social Learning Theory (SLT) in the 1960s. He conducted the well-known "Bobo doll experiment," in which children who observed adults acting aggressively toward a doll were likelier to replicate the same behavior. This experiment demonstrated that learning can occur through observation without direct reinforcement or practice.
Core Principles
The foundation of Social Learning Theory is built upon three fundamental principles that define how individuals acquire new behaviors and knowledge:
1. Observational Learning:
Observational learning involves watching others perform a task to understand how it's done. This process is especially effective when the observer focuses on someone they view as a role model—a teacher, peer, or public figure. By observing actions, strategies, and approaches, learners can mentally rehearse these behaviors before attempting them themselves. For instance, a student watching a peer solve a math problem on the board can gain insights into problem-solving techniques without directly engaging at that moment.
2. Modeling:
Modeling emphasizes the importance of demonstrating behaviors that others can replicate. Effective modeling doesn't just involve showing a task but also communicating the reasoning behind actions. For example, a teacher modeling good study habits by organizing tasks and managing time can inspire students to adopt similar practices.
3. Vicarious Reinforcement:
This principle highlights the impact of observing the outcomes of others' behaviors. Whether it's witnessing a classmate praised for answering a question or noting the negative consequences of disruptive behavior, learners internalize these experiences and adjust their actions accordingly. Learning from others' successes and mistakes is a powerful tool for personal growth without direct knowledge.
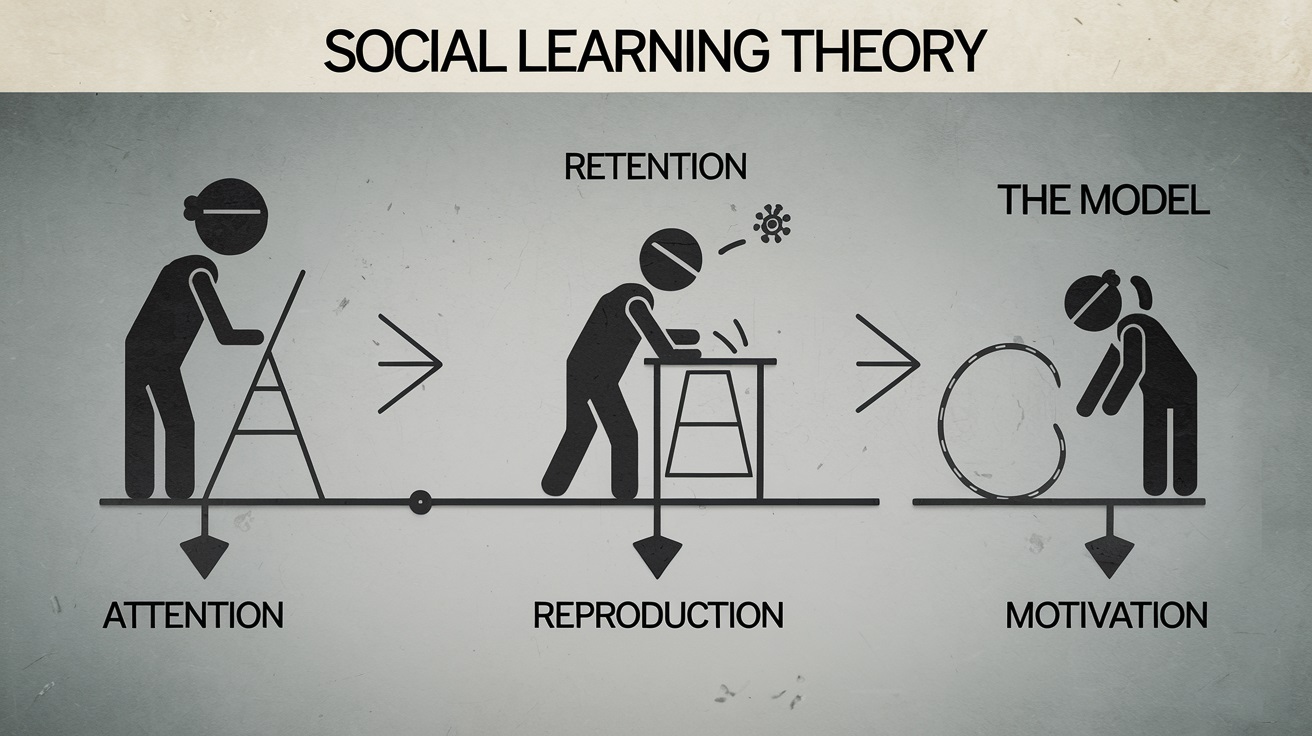
Four Stages of Learning

A 2022 study found that classrooms using collaborative learning strategies saw a 20% increase in engagement and a 30% improvement in retention rates.
Albert Bandura emphasized that effective modeling requires relatable role models. Teachers and peers who demonstrate achievable behaviors are more impactful than distant examples.
Bandura's model breaks learning into four stages:
-
Attention: The learner must focus on the behavior being modeled.
-
Retention: The behavior must be remembered for future replication.
-
Reproduction: The learner practices the behavior.
-
Motivation: The learner must be motivated to adopt the behavior, often influenced by perceived rewards or consequences.
These principles make Social Learning Theory particularly valuable in educational settings, where modeling and reinforcement are integral to teaching.
Benefits of Social Learning in Education
Benefits of Social Learning in Education
Social Learning Theory offers a multifaceted approach to enhancing education, encompassing cognitive, social, emotional, and behavioral benefits. Students engage in a more profound, meaningful learning experience by integrating observation and collaboration.
1. Cognitive Benefits
Enhanced Retention:
Learning becomes more effective when students observe actions and examples that bring abstract concepts to life. For instance, a math teacher solving problems on the board while explaining the steps provides a visual and auditory learning experience. This dual engagement improves memory retention, as students can associate the concept with a clear demonstration.
Critical Thinking:
Social learning encourages students to analyze observed behaviors and discuss their interpretations, fostering problem-solving and critical-thinking skills. Group discussions about complex topics, for example, allow students to evaluate multiple perspectives and develop well-rounded conclusions.
2. Social and Emotional Benefits
Improved Interpersonal Skills:
Collaborative learning activities like group projects and peer mentoring teach students to communicate effectively, delegate tasks, and work towards common goals. These experiences mirror real-world scenarios, preparing students for professional and personal interactions.
Empathy Development:
Observing diverse perspectives within a classroom helps students understand the emotions and experiences of others. For example, role-playing activities that simulate conflict resolution allow students to step into someone else's shoes, cultivating empathy and compassion.
3. Behavioral Development
Positive Behavior Modeling:
Students are more likely to replicate respectful and hardworking behaviors when teachers and peers model them. A teacher consistently showing patience during problem-solving sets a standard for perseverance that students can adopt.
Reduced Disruptions:
Social learning helps students understand the consequences of negative behaviors by observing their impact on others. For instance, when students see disruptive behavior leading to a loss of group privileges, they're less likely to repeat similar actions.
How to Apply Social Learning Theory in Education
1. Classroom Strategies
(A) Peer Learning
Encourage students to learn from one another through:
-
Group Activities: Divide the class into small groups for collaborative tasks like problem-solving or brainstorming.
-
Peer Feedback: Let students review each other's work, offering constructive suggestions.
(B) Role-Playing
Simulate real-life scenarios to teach skills such as conflict resolution or ethical decision-making. For example:
-
Have students act out a historical event to understand its context better.
-
Use role-playing to teach social skills, like negotiating or active listening.
(C) Storytelling
Teachers can share stories or examples to illustrate abstract concepts. For instance:
-
A science teacher could describe a famous experiment to demonstrate the scientific method.
-
Stories of personal struggle and success can inspire students to persevere.
2. Technology Integration
(A) Educational Videos
Platforms like YouTube or TED-Ed offer visual demonstrations that make learning engaging and relatable. For instance:
-
Use videos to show how geometric shapes apply in real-world architecture.
-
Share a tutorial on conducting a science experiment.
(B) Interactive Tools
Digital platforms such as Kahoot, Google Classroom, or Quizlet facilitate collaborative learning through games, quizzes, and discussions.
(C) Gamification
Introduce game-based learning to motivate students. Examples include:
-
Duolingo for language learning.
-
Prodigy Math for practicing arithmetic through gamified challenges.
3. Collaborative Learning Models
(A) Think-Pair-Share
Pose a question, have students discuss it with friends, and then share their findings with the class. This encourages participation and deeper thinking.
(B) Project-Based Learning
Students work together on projects, which is essential to apply knowledge creatively.
Examples:
-
Designing a website for a mock business.
-
Building a model bridge in an engineering class.
(C) Peer Mentorship
Pair advanced students with peers who need additional support. This reinforces the mentor's knowledge and builds confidence in both participants.
Case Studies and Real-Life Examples
In a high school physics class, students worked in teams to build and test a bridge model. Observing peers' approaches sparked creative problem-solving, while collaboration reinforced concepts like force and tension.
A teacher used role-playing to teach third-graders about empathy. Students acted out scenarios involving conflict resolution, helping them grasp the importance of listening and compromise.
A teacher introduced Kahoot quizzes before exams to review material in a fun, engaging way. Students reported feeling more confident and ready after participating.
Challenges and Solutions in Implementing Social Learning
Common Challenges
-
Teachers accustomed to traditional approaches may hesitate to adopt collaborative techniques.
-
Schools may need more tools or technology for interactive learning.
-
Group settings can be challenging for students with varying abilities.
Solutions
-
Provide training on social learning theory and implementation tools.
-
Use free or low-cost resources like open-source educational platforms.
-
Pair students based on complementary strengths to ensure balanced contributions.
Conclusion
Social Learning Theory (SLT) provides an insightful framework for making education more interactive, collaborative, and engaging. By integrating its principles into your teaching, you can transform your classroom into a space where students actively learn from one another and develop valuable cognitive, emotional, and behavioral skills.
Start small—try a group project or introduce a video-based lesson—and observe how your students respond. Over time, these strategies will help foster a more dynamic and inclusive learning environment. Remember, learning is inherently social, and every interaction in the classroom is an opportunity for growth.
FAQs
What is Social Learning Theory, in simple words?
It's a theory that explains how people learn by observing others, imitating behaviors, and indirectly experiencing consequences.
How can teachers apply Social Learning in classrooms?
Social learning in the classroom incorporates strategies like group projects, role-playing, and mentorship programs.
What are the benefits of peer collaboration?
It enhances critical thinking, teamwork, and communication skills while boosting confidence.
Is Social Learning effective in online education?
Yes, with tools like Zoom breakout rooms, educational videos, and interactive apps.
What are common barriers to implementing Social Learning?
Some common barriers include resistance to new methods, a need for more resources, and managing diverse learning speeds.
Education Social Learning Theory

