Secondary Level Curriculum of Subjective Examination - Physics Subject:
Teachers' Service Commission, Secondary Level Curriculum of Subjective Examination - 2076
Subject: Physics
Full Marks: 100
Time: 3 Hours
Section: A
Unit One: Mechanics
- Physical Quantity and Measurement: Error, precision, scalar, and vector products, addition and subtraction of vectors, resolution of a vector, vector differentiation and integration theorems, coordinate systems and differential operators in various coordinate systems
- Linear Motion: Equation of motion, projectile motion, and applications, Newton’s laws of motion and applications, conservation laws, work and energy, friction, elastic and inelastic collisions, power and efficiency
- Circular and Rotational Motion: Angular and linear velocity and acceleration, centripetal force, applications, rotational kinetic energy, a moment of inertia and its theorems, torque and angular acceleration of a rigid body, angular momentum, and its conservation, work, and power in rotational motion
- Gravitation: Kepler's laws of planetary motion, Newton’s law of gravitation, deduction of Newton’s law of gravitation from Kepler’s laws, a variation of ‘g’, mass and weight, the center of mass and center of gravity, motion of a satellite, rocket launching technology, geostationary satellite and parking orbit
- Oscillations: Equation of simple harmonic motion (SHM), linear restoring force, energy in SHM, the kinetic and potential energy of the mass-spring system, free, damped and forced oscillations and resonance
Unit Two: Mechanical Properties of Solids and Fluids
- Elasticity: Elasticity and plasticity, Hooke’s law, moduli of elasticity and determinations, elastic potential energy, the relationship among various elastic constants and applications in bending moments
- Fluid: Pressure, the variation of atmospheric pressure with altitude, Pascal’s law, Archimedes’ principle, pressure in a fluid, Nicholson’s hydrometer, molecular theory of surface tension, surface energy, angle of contact, capillarity and applications and theory of soap bubble
- Viscosity: Fluid dynamics, Newton’s formula, coefficient of viscosity, equation of continuity and its applications, Bernoulli's theorem and applications, Reynold's number, Poiseuille’s formula, Stoke’s law, and applications
- Hygrometry: Dew point, saturated and unsaturated vapor pressure, triple point, relative humidity and measurement, the effect of vapor pressure on boiling points
- Atmospheric Physics: Atmospheric phenomena, aerosol, and pollution, the ozone layer, greenhouse effect, acid rain
Unit Three: Heat and Thermodynamics
- Heat and Temperature: Concept of heat and temperature, temperature scales, the relationship among thermal expansivities and their determinations, absolute and apparent expansion of a liquid
- Thermal Properties of Matter: Specific heat capacity and measurement, Newton’s law of cooling, measurement of specific heat capacity of liquids by the method of cooling, change of phases, latent heat, specific latent heat of fusion and vaporization and their measurement, triple point and superfluidity
- Transfer of Heat: Conduction, convection, radiation, thermal conductivity and determination, convective coefficient, black-body radiation, Stefan-Boltzmann law, Wien’s displacement law, Planck’s radiation law, and Rayleigh-Jeans law
- Kinetic theory of Gases: Boyle’s law, Charle’s law, and ideal gas equation, derivation of pressure exerted by gas, Maxwell Boltzmann distribution of velocity, root mean square speed and Van der Wall’s
- Thermodynamics: Laws of thermodynamics, processes, heat capacities of an ideal gas and relation between them, isothermal and adiabatic processes for an ideal gas, heat engines and efficiency, refrigerator, entropy and disorder, Maxwell’s thermodynamic relations, Boltzmann factor, Bose-Einstein and Fermi-Dirac statistics
Unit Four: Optics
- Reflection: Laws of reflection, plane mirror, curve mirror, real and virtual images and determination of the focal length of curve mirror
- Refraction: Laws of refraction, refractive index and its determination, total internal reflection and its applications, optical fiber, refraction through a prism, white light spectrum, and dispersion
- Lenses: Spherical lenses, lens maker’s formula, power of a lens, a combination of thin lenses in contact, defect of vision, nature, and remedy, optical instruments, applications, and aberration at spherical surfaces
- Wave Nature of Light: Huygens’s wave theory and application, the velocity of light, interference, Young’s double-slit experiment, Fresnel’s biprism, Lloyd’s mirror, interference in thin-film, Newton’s ring, Michelson interferometer
- Diffraction and Polarization: Fresnel and Fraunhofer diffraction, zone plate, diffraction grating, dispersive and resolving power of a grating element, transverse nature of light, crystal polarizer, Malus law, Brewster’s law, production and analysis of polarized light, the principle of Nicola prism, optical activity and circular dichroism
Unit Five: Curriculum and Evaluation
- Curriculum and Textbook: Comparative study of physics curriculum, textbooks and teacher manual of Grade 11 and 12
- Teaching aids: Development and use of ICT (integrated commutation technology) in teaching physics
- Evaluation: Test items, marking scheme of physics of class 11 and 12 and specification grid
- Assessment: Continuous assessment system. grade and grading system
- Teaching Learning Science: Method of teaching, scientific method, a problem-solving method, demonstration method, discovery method, laboratory method, and cooperative learning method
Section B
Unit Six: Electrostatics & Electric Circuits
- Electrostatics: Electric charges, charging by induction, Coulomb’s law in electrostatics, electric field, lines of force, Gauss law and applications, electric potential, potential difference, equipotential surfaces, electron volt, potential gradient and field, electric dipole and quadrupole, the relation among D, E and P
- Capacitor: Capacitor and capacitance, parallel plate capacitor, a combination of capacitors, the energy of charged capacitor, the effect of a dielectric, types of capacitor, charging and discharging of capacitor
- Electric Circuits: Electric currents, Ohm’s law, electrical resistance, resistivity, conductivity, potential divider, superconductors, perfect conductors, conversion of galvanometer into voltmeter and ammeter, ohmmeter, the electromotive force of a source, internal resistance, Kirchhoff’s laws, Joule’s law and its verification, Wheatstone Bridge circuit, potentiometer and applications
- Thermo Electricity and Electrolysis: Seebeck, Peltier and Thomson effects, thermocouple, the variation of thermo e.m.f. with temperature, thermoelectric parameters, thermopile, Wiedemann-Franz law, Faraday’s laws of electrolysis and verification and Faraday’s constant
- Digital Electronics and Communications: Boolean algebra, the concept of logic Gates (OR, AND, NOT, NOR and NAND Gates, the concept of amplitude and frequency modulations, optical fiber communications)
Unit Seven: Electromagnetism
- Magnetism: Neutral points, calculation of magnetic moments and pole strength of a bar magnet, deflection magnetometer, vibration magnetometer, elements of earth magnetism and their variation, dip circle, permeability, susceptibility, hysteresis and types of magnetic materials
- Magnetic Field and Force: Magnetic field lines and magnetic flux, the force on moving charge and on a conductor, Lorentz force, torque on the rectangular coil, moving coil galvanometer, Hall Effect, the magnetic field of a moving charge, Biot and Savart law and applications, Ampere’s law and application
- Electromagnetic Induction: Faraday’s laws, induced emf, Lenz’s law, A generators, eddy currents, self-inductance and mutual inductance, energy stored in an inductor, transformer, ballistic galvanometer, search coil, Grassot’s flux meter, and earth inductor
- Maxwell’s Electromagnetic Equations: Maxwell’s equations and use in the propagation of the electromagnetic wave, derivation of Gauss’s, Faraday’s, Biot-Savart’s and Ampere’s law on the basis of Maxwell’s electromagnetic equations and pointing vector
- C. Circuit: Introduction, phasor, and phase diagram, AC through resistor R, inductor L and capacitor C and their series combinations, impedance and admittance, resonance in LCR series circuit and quality factor, wattless current and choke coil
Unit Eight: Acoustic and Quantum Mechanical Waves
- Basic Properties of Waves: Progressive and stationary waves, the principle of superposition, beats, velocity of sound wave in solid, liquid and gas, Newton’s formula for the velocity of sound in gas and Laplace correction and effect of a physical factor on the velocity of sound
- Acoustic Phenomena: Musical notes, overtones and harmonics, characteristics of sound, pressure amplitude, the intensity of sound, decibel unit, Doppler’s effect and applications, infrasonic and ultrasonic waves, noise pollution, acoustic of building and reverberation of sound
- Waves in Pipe and String: Waves in pipes, vibration in closed and open-end pipes, end correction, waves in the string, modes of vibration of a stretched string, laws of transverse vibration of the string and its verification
- Quantum Mechanics: De Broglie theory, wave-particle duality, uncertainly principle, Einstein’s photoelectric equation, Rutherford scattering, Bohr’s theory of hydrogen atom, spectral series, emission and absorption spectra, and Zeeman effect
- Quantum Mechanical Wave Propagation: Schrodinger’s wave equation, probability density, normalization of the wave function, solutions of Schrodinger equation for a free particle, potential step and infinite potential well
Unit Nine: Modern Physics
- Sub-Atomic Particles: Electron and its discovery, Milikan’s oil drop experiment, cathode rays, Thomson experiment, nuclear composition, properties of proton and neutron, isotopes, Einstein’s mass-energy relation, the binding energy of nucleus and nuclear
- Crystal Structures, Devices and Circuits: Basis and crystal structure, Bravais Lattices, cubic crystal structure, the difference between metals, band theory of solids, semiconductors, semiconductor diodes, and transistor and network theorems (Superposition, Thevenin and Norton)
- Radioactivity: Laws of radioactive disintegration, carbon dating, the energy released in nuclear fusion and fission, source of solar energy, a particle detector, particle accelerators, particles and antiparticles, baryons and leptons
- The Universe: Big bang and Hubble law, solar system, galaxy, neutron star, white dwarf, dark matter, black hole, and gravitational wave
- Special theory of Relativity: Lorentz transformations and addition of velocities, light cone, proper time and time dilation, covariance, and transformation of electromagnetic fields.
Unit Ten: Recent Trends in Physics
- Radio-Communications and Waves: Wireless communication, a global positioning system (GPS) and remote sensing, seismic waves, wave patterns of Gorkha earthquake 2015 and lightening
- Superconductor and Modern Technology: Meissner effect, types of superconductors, the BCS theory, cooper pair, superconductivity at high temperature, Josephson’s effect, holography, nanotechnology, integrated circuits, and applications
- Econo-Physics: Application of the theory of physics in economics, efficient market hypothesis and pioneering approaches
- Energy: Various sources of energy, renewable and nonrenewable energy, energy crisis and resolutions, energy and preservation of the environment, future needs and applications with reference to
- Medical use of nuclear and atomic radiations (MRI, CT-Scan, X-Rays, and Radiotherapy) and possible health hazards
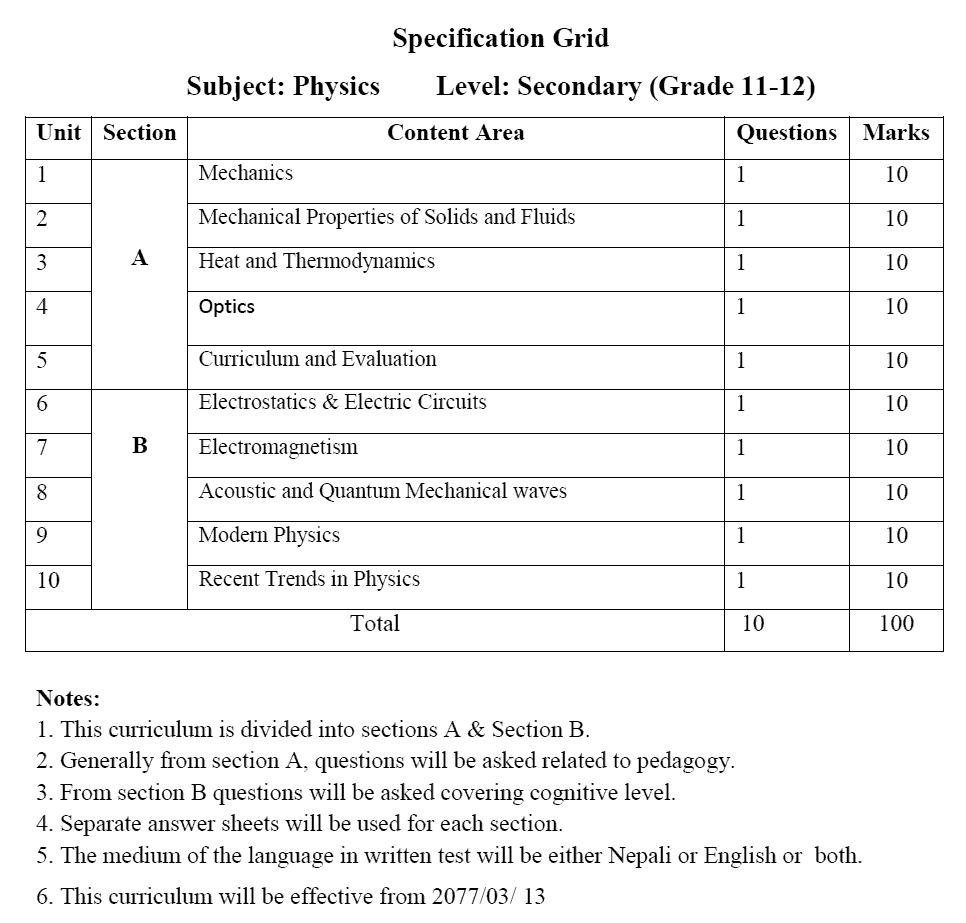
Specification Grid
Subject: Physics
Level: Secondary (Grade 11-12)
|
Content Area |
Questions |
Marks |
|
Section - A |
||
|
Unit 1: Mechanics |
1 |
10 |
|
Unit 2: Mechanical Properties of Solids and Fluids |
1 |
10 |
|
Unit 3: Heat and Thermodynamics |
1 |
10 |
|
Unit 4: Optics |
1 |
10 |
|
Unit 5: Curriculum and Evaluation |
1 |
10 |
|
Section - B |
||
|
Unit 6: Electrostatics & Electric Circuits |
1 |
10 |
|
Unit 7: Electromagnetism |
1 |
10 |
|
Unit 8: Acoustic and Quantum Mechanical waves |
1 |
10 |
|
Unit 9: Modern Physics |
1 |
10 |
|
Unit 10: Recent Trends in Physics |
1 |
10 |
|
Total |
10 |
100 |
Notes:
1. This curriculum is divided into sections A & Section
2. Generally from section A, questions will be asked related to
3. From section, B questions will be asked covering cognitive
4. Separate answer sheets will be used for each
5. The medium of the language in the written test will be either Nepali or English or
6. This curriculum will be effective from 2077/03/ 13


