Secondary Level Biology Subject Curriculum of Subjective Examination - 2076
Government of Nepal, Teachers' Service Commission
Secondary Level Curriculum of Subjective Examination - 2076
Subject: Biology
Marks: 100
Time: 3 Hours
Section - A
Unit One: Bimolecular, Cell Biology and Embryology
- Bimolecular: Carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, minerals, enzymes and
- Cell -Biology: Concepts of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, the detailed structure of eukaryotic cells, and significances.
- Plant Anatomy: Types of plant tissues, the anatomy of dicot and monocot root, stem and leaf
- Animal Tissues: Types, structure, functions, and locations
- Embryology: Asexual and sexual reproductions in angiosperms, pollination, fertilization, development of male and female gametophytes, development of dicot and monocot embryos, the concept of endosperm, and gametogenesis
Unit Two: Bio-Diversity
- Introduction: Five kingdom classification systems (monera, Protista, fungi, plantae and animalia).
- Fungi (mucor and yeast) and Algae (spirogyra): Structure, reproduction, and economic importance
- Morphological structure and reproduction of marchantia, dryopteris and pinus, economic importance of bryophytes, pteridophytes and
- Protista: Protozoa (diagnostic features and classification up to class)
- Animalia: Systems (digestive, excretory, nervous, reproductive) and economic importance of earthworm and systems (digestive, blood vascular, respiratory and reproductive) of frog
Unit: Three: Genetics and Ecology
- Genetics: Genetic materials (DNA and RNA), Mendelian genetics, linkage and crossing over, mutation and
- Ecology: Ecosystem and ecology, ecological adaptation, ecological
- Biota and Environment: Animal adaptations, environmental pollution, pesticides, and their effects
- Conservation Biology: Concept of biodiversity, biodiversity conservation, national parks, wildlife reserves, conservation areas, biodiversity hotspots, wetland, and Ramsar sites, causes of extinction and conservation strategies
- Vegetation: Types of vegetation in Nepal, the concept of In-situ (protected areas), and Ex-situ (botanical garden, seed bank) conservation.
Unit: Four: Plant Physiology and Human Biology
- Plant Physiology: Water relation, photosynthesis and respiration, plant hormones, plant growth, and movement
- Human Biology: Human Systems (digestive, respiratory, circulatory, excretory, nervous and reproductive) Sense Organs and Endocrinology
Unit Five: Overview of Science Curriculum and Evaluation of Secondary Level
- Curriculum and Textbook: Comparative study of physics curriculum, textbooks and teacher manual of Grade 11 and 12
- Teaching aids: Development and use of ICT (integrated commutation technology) in teaching biology
- Evaluation: Test items, marking scheme of the biology of class 11 and 12 and specification grid
- Assessment: Continuous assessment system, grade, and grading system
- Teaching Learning Science: Science process skills, scientific method, approaches of teaching science, science laboratory and safety measures
Section - B
Unit Six: Microbiology and Applied Biology
- Monera: Introduction, structure of bacterial cell, mode of nutrition, bacterial growth, cyanobacteria (blue-green algae) and virus (introduction, structure importance) and bacteriophage
6.2 Impacts of Biotechnology in the field of Microbiology.
- Applied Biology: Tissue and organs transplantation, in-vitro fertilization (IVF), amniocentesis, the concept of genetically modified organisms, poultry, and fish farming,
- Application of cross-fertilization, self and cross-pollination, cryopreservation, and mutation.
- Biotechnology: Tissue culture, plant breeding, disease resistance plants, green manure and bio-fertilizer, bio-pesticide, genetic engineering and GMOs and application, bio-engineering, food safety, and food security
Unit Seven: Animal Taxonomy and Nomenclature
- Lower Non-Chordata: Taxonomy (concept, trends, species, keys/diagnostic features), structure and reproduction (Porifera, Coelenterata, Platyhelminthes, aschelminthes, and Annelida)
- Higher Non-Chordata and Protochordata: Diagnostic features, classification, structure and organ systems (Arthropoda, Mollusca, Echinodermata, and protochordate)
- Chordata: diagnostic features, classification, origin, evolution and adaptive radiation of Chordata (Pisces, amphibia, reptilia, aves, and Mammalia)
Unit Eight: Plant Taxonomy and Nomenclature
- Plant Taxonomy: Principles, approaches of classification, and botanical nomenclature.
- Angiosperm Phylogeny Group (APG): Classification, principles, and ranks with major angiosperm clades, with an updated version
- Taxonomic Description of the Families: Brassicaceae, Fabaceae, Solanaceae, and Liliaceae with economic
Unit Nine: Anatomy, Evolution, Biogeography, and Ecology
- Comparative Anatomy of Chordate: Exoskeleton, endoskeleton, digestive organs, respiratory organs, circulatory organs, portal systems, urinogenital organs, gonads, ducts, and brain
- Evolution: Life and its origin (Oparin-Haldane theory, Miller and Urey's experiment), principles of organic evolution, basic patterns of evolution- sequential and divergent evolution, micro, macro, mega and quantum evolution, the modern synthetic theory of evolution, gene pool and gene frequency, Hardy- Weinberg Law
- Biogeography: Biogeography and distribution, biogeographic patterns and process, zoogeographic realms, the theory of island biogeography, zoogeographic affinities of the fauna of Nepal
- Ecology: Population growth models, community patterns, measurement and analyses methods of population and communities
Unit Ten: Neuronal, Behavioral Biology, Immunology, Cytogenetic, Biostatistics, and Bioinformatics
10.1. Neurobiology: Organization of the nervous system, cells and connection of the nervous system, neurotransmitters and neuropeptides, neural regulation of complex functions, brain functions, consciousness, biorhythm and its regulatory genes/circadian timekeeping, sleep, dreaming and wakefulness, reward, addiction, and emotion
- Behavioral Biology: Principles, mechanisms and development of animal behavior, stimuli and communication, learning and memory (bees, birds, primates), the ecology of feeding behavior and mating systems and ecology of parental care
- Immunology and Microbial Diseases: Immune system, receptors, nature of antigen and antibody, immune effectors mechanisms, major histocompatibility complex (MHC) genes, and products, risk and hazard group of microorganisms, causative agents, symptoms, prevention and control measures of selected human diseases (tuberculosis and HIV, SARS, COVID-19, hepatitis) and basic concepts of immunology–vaccines
- Cytogenetic: Cell membrane transport mechanism, cell metabolism, cell adhesion and communication, structural organization of genome, structure, expression, and regulation of genes
- Biostatistics & Bioinformatics: Databases, tools and their uses (structure, importance, nucleic acid, and protein sequence), evolutionary trees homology and similarity, phylogeny and relationship (approaches used in phylogenetic analysis, phylogenetic trees)
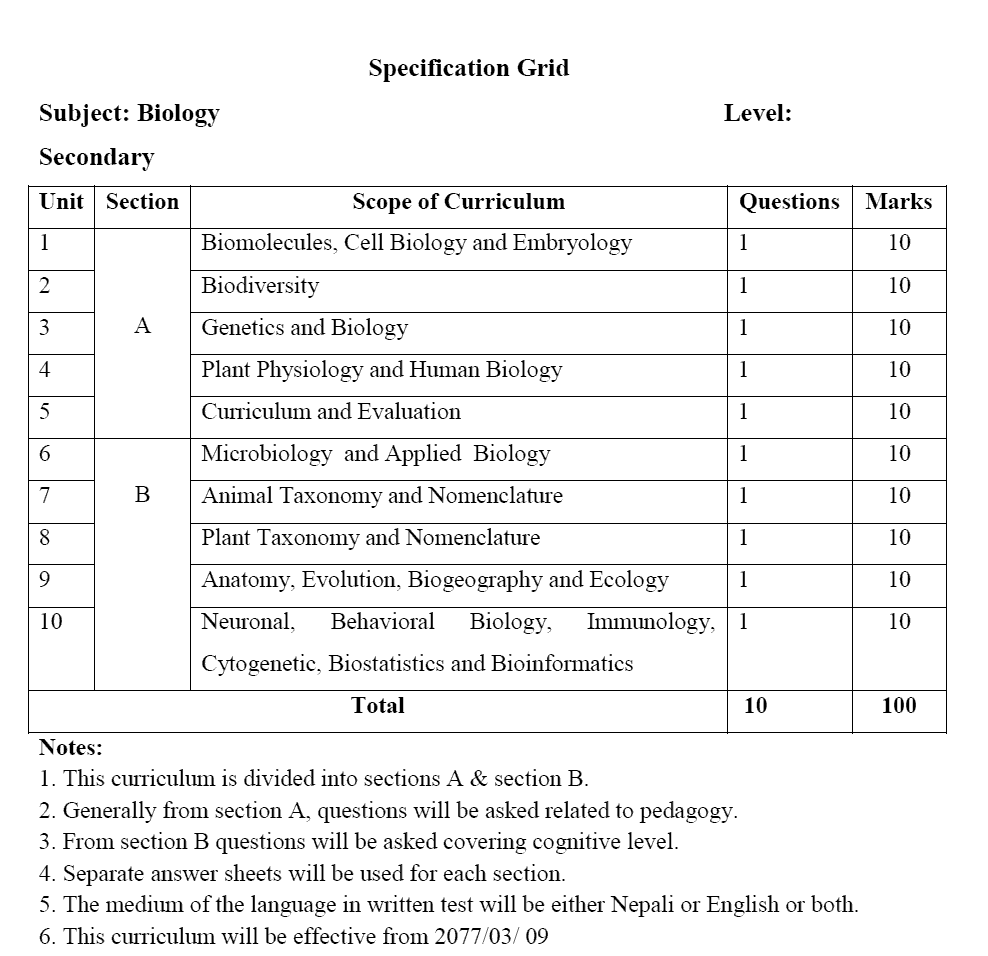
Specification Grid
Subject: Biology
Level: Secondary
|
Scope of Curriculum |
Marks |
|
Section - A |
|
|
Unit 1: Biomolecules, Cell Biology and Embryology |
10 |
|
Unit 2: Biodiversity |
10 |
|
Unit 3: Genetics and Biology |
10 |
|
Unit 4: Plant Physiology and Human Biology |
10 |
|
Unit 5: Curriculum and Evaluation |
10 |
|
Section - B |
|
|
Unit 6: Microbiology and Applied Biology |
10 |
|
Unit 7: Animal Taxonomy and Nomenclature |
10 |
|
Unit 8: Plant Taxonomy and Nomenclature |
10 |
|
Unit 9: Anatomy, Evolution, Biogeography, and Ecology |
10 |
|
Unit 10: Neuronal, Behavioral Biology, Immunology, Cytogenetic, Biostatistics, and Bioinformatics |
10 |
|
Total |
100 |
* One question from each unit and 10 Marks for each question
Notes:
1. This curriculum is divided into sections A & section
2. Generally from section A, questions will be asked related to
3. From section, B questions will be asked covering cognitive
4. Separate answer sheets will be used for each
5. The medium of the language in the written test will be either Nepali or English or
6. This curriculum will be effective from 2077/03/ 09


